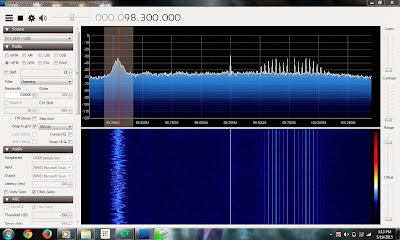
Till now we have seen how to use the rtl-sdr dongle but what if you can't afford one or forgot your at home. sdr.hu is great website which allows you to access open sourced sdr receivers around the world. This helps you to study software defined radio even without owning it.
 To get access to a sdr dongle which is openly hosted you can select any one of the receivers from the huge list. The receivers are voted by the users as per their performance. You might not be able to get the entire radio spectrum as the receivers vary from provider to provider. The deceives may work or not as these devices are not installed by the website or maintained by it. This might not be helpful for IOT(internet of things) testing. This can be a great starter kit as it can help a noob to learn the basics about SDR. While using it we found that some of the devices were a bit slow or it might just be my internet connection. The "how to?" is quite easy hence help your self around. It's as easy as opening a website and going around it.
To get access to a sdr dongle which is openly hosted you can select any one of the receivers from the huge list. The receivers are voted by the users as per their performance. You might not be able to get the entire radio spectrum as the receivers vary from provider to provider. The deceives may work or not as these devices are not installed by the website or maintained by it. This might not be helpful for IOT(internet of things) testing. This can be a great starter kit as it can help a noob to learn the basics about SDR. While using it we found that some of the devices were a bit slow or it might just be my internet connection. The "how to?" is quite easy hence help your self around. It's as easy as opening a website and going around it. Note:-
If you are using a proxy then you might have to stop it or use a VPN to bypass it.